Leave Your Message
Abrasion Resistant Steel plays a critical role in various industrial applications, especially in sectors where durability and resistance to wear and tear are paramount. According to the latest market reports, the global demand for abrasion resistant steel is projected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing need for high-performance materials in mining, construction, and heavy equipment industries. For instance, a report from the World Steel Association notes that enhancements in steel compositions and manufacturing processes have led to the development of advanced abrasion resistant steel grades that offer superior performance in challenging environments.
Choosing the right type of abrasion resistant steel for specific projects involves understanding the unique operational demands and the environmental conditions that the materials will face. Factors such as hardness, toughness, and overall impact resistance must be carefully evaluated to ensure that the steel chosen will not only meet the performance requirements but also optimize cost-effectiveness over the material’s lifespan. Industry experts highlight that making informed decisions based on thorough research and analysis can lead to significant reductions in maintenance costs and downtime, as well as improved safety in operations. As such, professionals must remain informed about the latest advancements and applications of abrasion resistant steel to make the best choices for their projects.

Abrasion-resistant steel (AR steel) is a specific type of steel designed to withstand wear and tear in demanding environments. Its unique properties make it ideal for a variety of applications, including mining, construction, and material handling. According to industry reports, the global demand for AR steel is projected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing need for durable materials that can reduce downtime and maintenance costs. This steel is engineered with a hardness range typically between 200 to 650 Brinell, striking a balance between toughness and abrasion resistance.
In many applications, such as with excavators or dump trucks, AR steel provides essential performance advantages. The Oak Ridge National Laboratory highlighted that using AR steel components in heavy machinery can decrease operational costs by up to 30% due to their extended lifespan compared to conventional steels. Moreover, industries like mining are adopting AR steel for its ability to withstand the harsh conditions present in these environments, resulting in less frequent replacements and lower material waste. By understanding the specific grades of abrasion-resistant steel and their applicable uses, companies can better align their project needs with the right materials, enhancing efficiency and sustainability within their operations.
This chart illustrates the comparison of various types of abrasion resistant steels based on their hardness and typical applications.
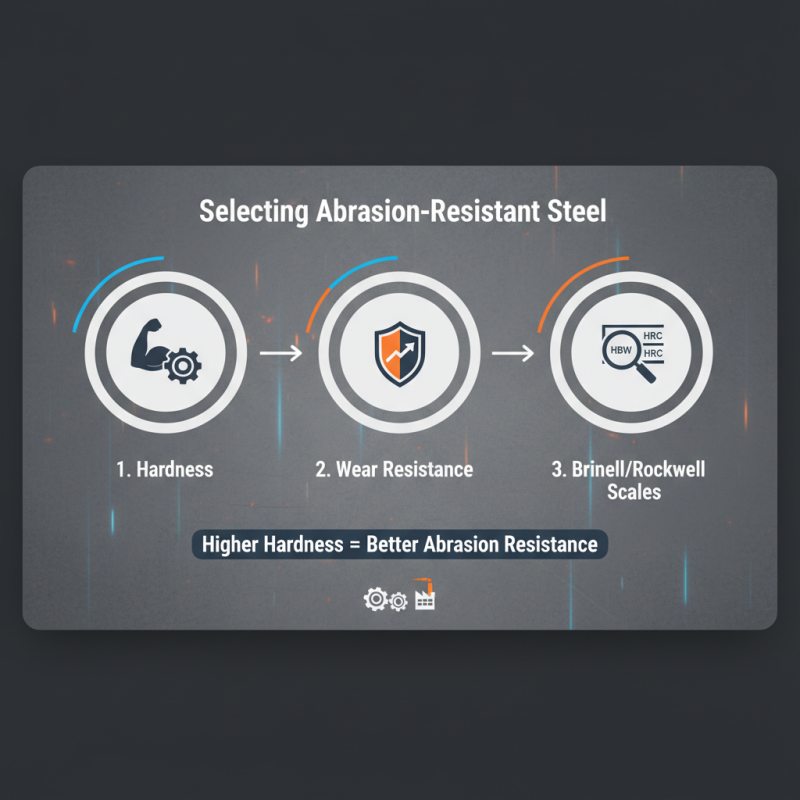
When selecting abrasion-resistant steel for your project, it's crucial to evaluate several key properties. First, consider the hardness of the steel. Hardness is a fundamental characteristic that influences wear resistance; the higher the hardness, the better the material can withstand abrasive conditions. Look for specifications that indicate hardness ratings, usually measured on the Brinell or Rockwell scales, which can help in identifying the best material for your application.
Another important factor is the toughness of the steel. Toughness refers to the material's ability to absorb energy and deform plastically without fracturing. This characteristic is crucial in environments where impact and stress are prevalent. Ensure that the steel you choose balances hardness with toughness, as overly hard materials may become brittle.
**Tips:**
- Always assess the specific conditions your steel will encounter, such as temperature changes, types of abrasives, and loading conditions.
- Consult with suppliers about the available heat treatments and coatings that can enhance the abrasion resistance of the selected steel, offering additional protection where necessary.
When selecting abrasion resistant steel for various applications, it is crucial to understand the different types available and their specific uses. There are two main categories of abrasion resistant steel: high-carbon steel and alloy steel. High-carbon steel typically contains more carbon content, leading to increased hardness and wear resistance. It is often employed in industries that require equipment to withstand scraping and gouging, such as mining, construction, and agricultural machinery.
On the other hand, alloy steels are engineered with additional elements like chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, enhancing their toughness and ductility. These steels are ideal for applications where both abrasion resistance and impact resistance are necessary. For example, they are commonly used in the manufacturing of heavy-duty conveyor systems, bucket excavators, and crushing equipment. By understanding these distinctions, manufacturers can make informed decisions tailored to the specific demands of their projects, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of their machinery.
| Type of Abrasion Resistant Steel | Hardness (BHN) | Typical Applications | Heat Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR400 | Hardness: 360-440 BHN | Construction, mining equipment | Not typically heat treated |
| AR500 | Hardness: 450-540 BHN | Armor plates, chutes | Can be quenched and tempered |
| AR600 | Hardness: 550-700 BHN | Heavy-duty applications, mining tools | Typically not heat treated |
| Hardox 400 | Hardness: 350-400 BHN | Dump trucks, excavators | Can be heat treated |
| Hardox 500 | Hardness: 450-500 BHN | Wear plates, rock crushers | Can be quenched and tempered |
When selecting abrasion resistant steel, understanding the factors that influence its cost and availability is crucial for project success. One primary factor is the raw material costs, which have seen significant fluctuations due to global market dynamics. According to an industry report by the World Steel Association, the price of alloying elements such as chromium and molybdenum can vary greatly due to changes in supply and demand, directly impacting the production costs of abrasion resistant steel. As of 2023, these fluctuations have resulted in price variances of up to 15% in certain regions, necessitating careful consideration during project budgeting.
Another pivotal factor is regional availability, which can be influenced by transportation costs, local demand, and manufacturing capabilities. The Steel Market Development Institute reports that certain areas may face shortages of specific grades of abrasion resistant steel due to high local demand or export restrictions, further complicating sourcing strategies. Additionally, the lead time for production and delivery can be affected by these availability issues, with some projects experiencing delays up to eight weeks if alternative suppliers are necessary. Evaluating these elements early on can provide a clear understanding of how they influence both the budget and timeline for projects involving abrasion resistant steel.
When it comes to working with abrasion resistant steel, proper fabrication and maintenance are key to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. According to recent industry reports, utilizing the right cutting techniques and tools can significantly affect the integrity of abrasion resistant materials. For instance, plasma cutting is often recommended over traditional methods, as it produces less thermal distortion, maintaining the steel's hardness and wear resistance. Additionally, using proper clamping methods during fabrication can prevent unnecessary warping.
Tips: Always ensure that the cutting equipment is well-maintained and calibrated. Regular checks can increase precision and reduce waste, leading to cost efficiencies in your project. Furthermore, before beginning fabrication, reviewing and understanding the specific properties of the steel grade being used is crucial. Different grades may have varying toughness and abrasion resistance, which will directly impact their performance based on the application.
Maintenance of abrasion resistant steel is just as critical as its initial fabrication. Regular inspections and timely repairs can prevent extensive damage and prolong the life of the steel. Industry statistics suggest that proactive maintenance practices can lead to a decrease in equipment downtime by up to 30%. Implementing a routine inspection schedule, which includes checking for surface wear and potential cracks, ensures that issues are addressed before they escalate, thus maintaining safety and efficiency in operations.
Tips: Adopt a structured maintenance plan that schedules inspections at regular intervals based on the environment and usage levels of the steel. Utilizing monitoring technologies can also aid in identifying wear patterns and planning maintenance activities appropriately.